Updated Dec 12, 2025 14 min read
Data Warehouse Testing Strategy: Your Ultimate Guide
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential components of building and executing a successful data warehouse testing strategy. We will explore the core phases, discuss the specific testing types required, highlight the challenges you'll face, and outline the tools and best practices to ensure your data warehouse is a reliable source of truth for your project.

For most companies, the cost of insufficient data impacts 15% to 25% of overall business revenue. On a macro level, poor data quality costs the U.S. economy $3.1 trillion annually. Along with this financial hit, one in three business leaders do not trust their company’s data. After understanding the drastic negative impact of unreliable data, it makes sense why ensuring the veracity and integrity of data has quickly assumed high priority.
What is the most logical first step to testing data quality? Starting in your data warehouse, where all the puzzle pieces come together. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential components of building and executing a successful data warehouse testing strategy. We will explore the core phases, discuss the specific testing types required, highlight the challenges you'll face, and outline the tools and best practices to ensure your data warehouse is a reliable source of truth for your project.
What is a Data Warehouse Testing?
Data warehouse testing encompasses building and executing data test case strategies to ensure that all data in the warehouse is complete, accurate, and consistent within the organization’s data framework. Primarily used to validate the reliability of analytical data within an organization, ensuring the trustworthiness of its overall business insights. DW testing includes data, reports, and dashboards, which are frequently used to make critical business decisions, making them crucial components of data warehouse testing.
Unlike traditional application testing, data warehouse testing involves unique challenges and methodologies due to the complexity of data systems, large-scale data handling, and multi-source data integration.
The High Cost of Missing Data Warehouse Testing
The consequences of deploying an untested or poorly tested data warehouse can be severe and far-reaching:
- Flawed Business Decisions: If BI reports are based on inaccurate or incomplete data, executives may make strategic decisions that hurt revenue, misallocate resources, or miss market opportunities.
- Erosion of User Trust: When business users and analysts discover data inconsistencies, they lose confidence in the entire BI system. This leads to low adoption rates and a return to siloed, less reliable data analysis methods.
- Increased Maintenance Costs: Fixing data issues in a production environment is significantly more complex and expensive than catching them during development. It often requires re-running large ETL jobs, correcting historical data, and extensive debugging.
- Compliance and Regulatory Risks: In industries such as finance and healthcare, data accuracy is a legal requirement. Data errors can lead to failed audits, hefty fines, and reputational damage.
Overview of Data Warehouse Components
Let’s understand each of the components of a data warehouse in detail:

- Data Sources: This component encompasses the various systems and databases from which data is collected. Examples include CRM platforms, ERP systems, IoT devices, spreadsheets, and other external or internal data sources. These inputs form the foundation of the data warehouse.
- Staging Area: A temporary storage space where raw data from different sources is initially loaded. The staging area is crucial for data cleansing, transformation, and validation. These steps ensure the quality and consistency of the data before it moves to the main storage.
- Storage Layer: This is where the processed data is stored in the warehouse. The storage layer holds the cleansed and transformed data in a structured format optimized for analytical queries and reporting.
- Metadata Manager: Responsible for managing the metadata in the warehouse, which includes information about data definitions, lineage, relationships, and transformations. Metadata provides context and ensures that data is well-organized and traceable.
- Data Marts: A data mart is essentially a smaller, more focused version of a data warehouse. While a data warehouse holds a company’s entire data, a data mart stores only the data related to a specific area of the business, like marketing, sales, or finance.
- Presentation Layer: The interface between the data warehouse and end-users. It includes tools such as reporting applications, dashboards, query interfaces, and BI systems that allow users to access and analyze data meaningfully.
What is a Data Warehouse Testing Strategy?
A data warehouse test strategy is a structured approach that outlines the methods and processes for testing a data warehouse to ensure its functionality, accuracy, performance, and security. The strategy aims to verify that the data warehouse is functioning correctly, delivering accurate data, and meeting the business requirements it was built to support. It involves testing various components of the data warehouse system, including the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, data storage, reporting, and data retrieval.
Why a Data Warehouse Testing Strategy is Non-Negotiable?
According to Forbes, poor-quality data costs organizations an average of $12.9 million per year, a number cited initially in Gartner’s research and still relevant in 2025 as one of the primary operational risks for global enterprises. Harvard Business Review adds that insufficient data costs the U.S. economy nearly $3 trillion annually, creating hidden inefficiencies that undermine strategic decision-making. These numbers highlight a fundamental truth: a modern enterprise cannot rely on analytics, AI, or business intelligence without a strong data warehouse testing strategy.
Treating data warehouse testing as an ad-hoc activity at the end of a development cycle is a recipe for disaster. The sheer volume and complexity of data make a structured, proactive approach essential. A DWH testing strategy provides a roadmap for ensuring data integrity, accuracy, and performance from the ground up.
A data warehouse test strategy ensures the system is thoroughly tested across all critical components, including data extraction, transformation, loading, and reporting. By focusing on key areas such as data integrity, performance, and security, businesses can ensure their data warehouse operates smoothly and delivers accurate, reliable data to support decision-making. Now, let's consider effective strategies for testing data warehouse applications.

Effective Strategies for Testing Data Warehouse Applications
Testing data warehouse applications requires careful planning and implementing strategies that address specific challenges, such as large data volumes, complex transformations, and data security. Several strategies for testing data warehouse applications can be employed to ensure the data warehouse operates effectively and meets business requirements.
Data Sampling
Instead of testing the entire dataset, data sampling involves selecting a representative subset of data for testing. This helps speed up the testing process while still providing accurate results. It’s an efficient method to ensure that various data scenarios are tested without overwhelming the system.
Automated Testing
Automation tools can streamline testing efforts, especially for repetitive tasks like data validation, performance testing, and regression testing. Tools like Apache JMeter can be used to automate testing workflows, improving efficiency and reducing human error( learn how automated functional testing saves time, improves accuracy, and ensures robust software functionality. Discover practical steps to implement it effectively for your projects in our latest article).
End-to-End Testing
End-to-end testing is crucial for ensuring that all data warehouse components work together seamlessly. This includes verifying the accuracy of data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes and ensuring that data flows correctly from the source systems to the data warehouse.
Data Security Testing
Ensuring the security of sensitive data is vital during testing. Techniques such as data masking, encryption, and proper access controls can prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations during testing.
Performance Testing
Testing how the data warehouse performs under different loads is critical. Performance testing ensures the system can scale and deliver data within required timeframes.
As the complexity and volume of data increase, automation plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and consistency of data warehouse testing. Automating routine and repetitive tasks allows faster validation and ensures higher accuracy in data integrity, performance, and transformation processes. Let’s explore the data warehouse automation testing strategy, focusing on effectively integrating automation into your testing workflows for better results.
The Role of Automation in DWH Testing
Given the repetitive nature of data validation and the enormous scale of the data involved, manual testing focuses on aspects that automated testing can't cover. These include visual application checks and the ability to test specific user experience-based scenarios that are impractical to automate. On the other hand, automated testing offers advantages in speed and repeatability. Automated testing eliminates the human factor, allows you to reuse the same scenarios, and is much faster than manual testing.
A modern data warehouse test strategy must heavily incorporate automation. Implementing a robust data warehouse automation testing strategy provides significant benefits:
- Increased Efficiency and Speed: Automated scripts can execute thousands of checks across millions of records in a fraction of the time it would take a human tester. This accelerates the feedback loop for developers.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Repeatability: Automated tests are executed consistently, eliminating the risk of human error. This is crucial for regression testing, where the same tests must be run repeatedly.
- Facilitation of CI/CD: Automated testing is a cornerstone of Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Tests can be automatically triggered whenever new ETL code is committed, providing immediate feedback on its quality.
What to Automate?
While the goal is to automate as much as possible, some tests provide a higher return on investment for automation:
- Record Count Validations: Automate scripts that compare row counts between source, staging, and target tables.
- Aggregate Validations: Scripts that compare sums, averages, or other aggregate functions on key numeric columns.
- Data Transformation Checks: For deterministic rules, scripts can take a sample input, apply the transformation logic, and compare the result with the ETL output.
- Regression Test Suites: The entire regression suite should be automated to run after every build or deployment.
- Metadata Checks: Scripts can query the database's system catalog to validate table structures, data types, and constraints against the design specifications.
Tools and Frameworks for Automated Testing
A variety of tools and frameworks can support your automation efforts. These range from general-purpose scripting languages to specialized data testing platforms. DWH testing tools automate testing processes for data-centric systems.
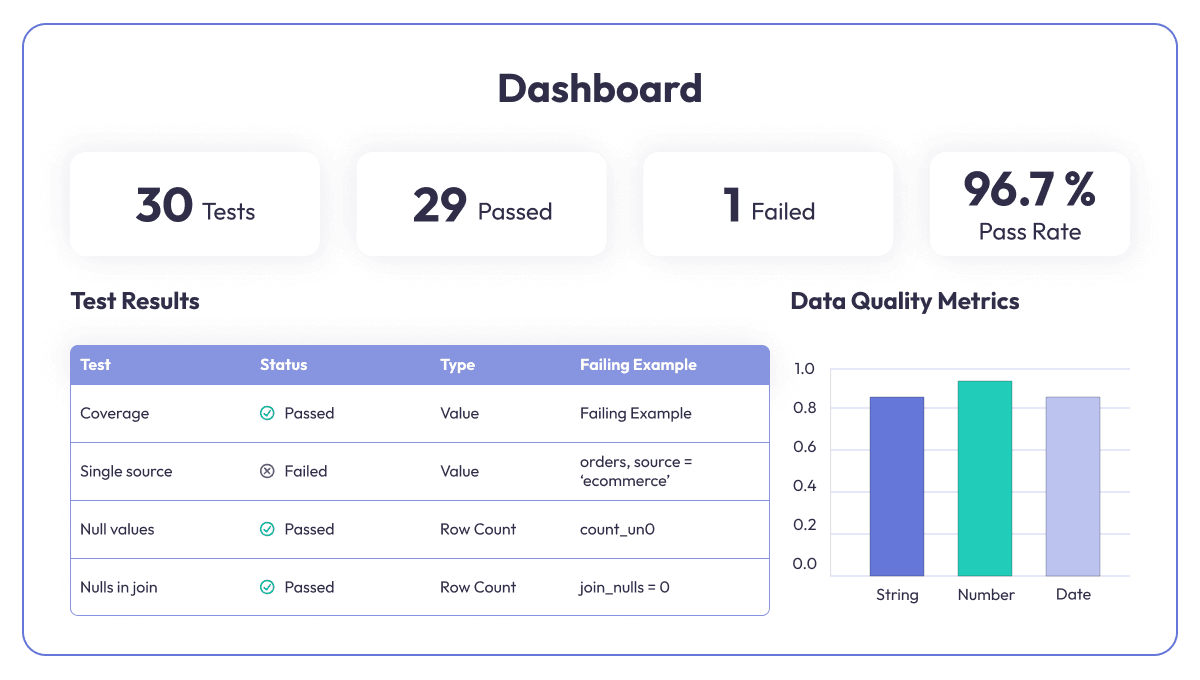
A dashboard test results and data quality metrics.
Best Practices for Effective Data Warehouse Testing
Here are some best practices for effective data warehouse testing:
- Clear test objectives: Define clear testing goals, such as data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and data integration.
- Data profiling and analysis: Before testing, use data profiling tools to understand data characteristics, anomalies, and patterns.
- Comprehensive test coverage: Includes unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and end-to-end validation.
- Automated testing: Automate repetitive testing tasks (e.g., data validation, data comparison, ETL processes).
- Data security testing: Ensure that sensitive data is protected during testing, including data masking and encryption.
- Regression testing: Continuously test changes to ensure they don’t negatively impact existing data integrity.
- Regular data updates and revalidation: Update test data regularly to mirror production data and validate changes.
- Detailed documentation and reporting: Maintain clear documentation of test cases, test results, and data issues.
- Continuous monitoring and feedback loop: Regularly review test results and incorporate feedback into future testing processes.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure an efficient, and reliable data warehouse testing process that guarantees high-quality data and system performance.
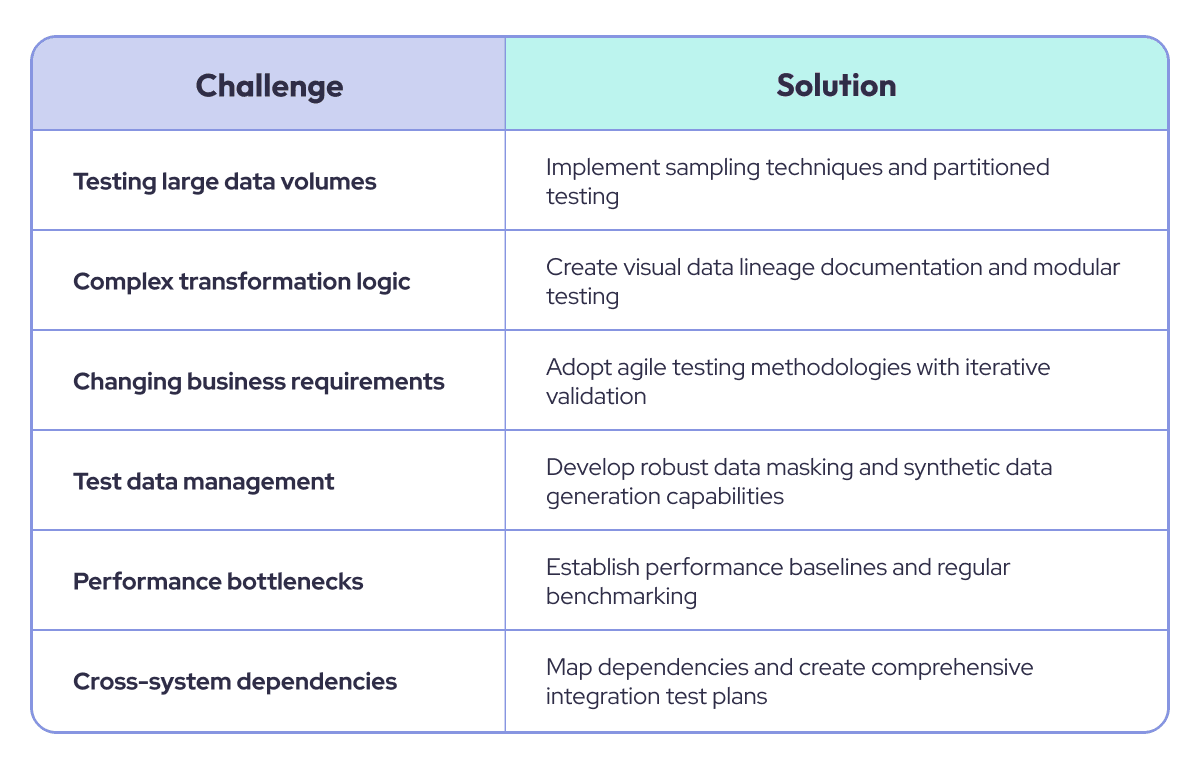
Common Challenges and Solutions in DWH Testing Strategy
Let's have a look at some common challenges and solutions in DWH testing strategy
Why Businesses Need a Data Warehouse Testing
Data warehouse testing is vital in enabling accurate reporting and effective business analytics. It offers significant benefits that drive better data management and decision-making:
- Centralized data storage: Consolidates data from multiple sources into a secure repository.
- Advanced reporting and complex queries: Enables businesses to generate detailed reports and handle complex analytical queries.
- Data standardization: Converts data into a unified format, even from legacy systems, improving usability and consistency.
- Data cleaning and deduplication: Identifies and removes duplicate, corrupted, or inaccurate data sets, ensuring higher data quality.
- Faster data processing: Reduces the overall time needed for data analysis and reporting.
- Historical data retention: Stores large volumes of historical data for long-term analysis and trend identification.
A data warehouse test strategy helps businesses make informed decisions by ensuring data integrity, improving analysis efficiency, and providing a comprehensive view of historical and current trends. This capability ultimately drives better strategic planning and operational success.
Conclusions
A data warehouse testing strategy is a crucial aspect of data management, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of data for decision-making. It is essential to implement a comprehensive testing strategy that encompasses data integration, quality, performance, and security to maintain the data warehouse's credibility. Your data is your business's backbone - don’t leave its quality to chance. Contact us to ensure your data warehouse is robust, reliable, and ready to drive your success.
Your data is your business's backbone - don’t leave its quality to chance. Contact us to ensure your data warehouse is robust, reliable, and ready to drive your success.
Comments
There are no comments yet. Be the first one to share your opinion!
For 8 years, we have helped more than 200+ companies to create a really high-quality product for the needs of customers.
- Quick Start
- Free Trial
- Top-Notch Technologies
- Hire One - Get A Full Team
Was this article helpful to you?
Looking for reliable Software Testing company?
Let's make a quality product! Tell us about your project, and we will prepare an individual solution.
Testing a data warehouse involves validating the data, ensuring its accuracy, consistency, and completeness, and verifying the performance of queries and reports. Key activities include ETL testing (validating data extraction, transformation, and loading), data validation (ensuring data consistency across different sources and targets), and performance testing (ensuring efficient query processing and report generation).
The strategy of ETL testing involves verifying the extraction, transformation, and loading processes of data from source systems to the data warehouse. This includes testing data accuracy, ensuring transformations are applied correctly, validating data integrity during the load process, and ensuring the data loaded matches the expected results. It also involves checking for data completeness and handling edge cases.
Data warehouse testing and ETL testing are not the same, though they are closely related. Data warehouse testing focuses on verifying the overall data warehouse structure, including data quality, performance, and reporting. On the other hand, ETL testing is a subset that focuses explicitly on validating the ETL processes that extract, transform, and load data into the warehouse, ensuring that the data is accurate and consistent throughout these stages.
A data warehouse test strategy document is a formal plan that serves as the master guide for all testing activities. It defines the testing scope, objectives, and methodologies. It outlines the types of testing to be performed (e.g., performance, data completeness), the tools and environments to be used, resource allocation, schedules, and the criteria for test entry and exit. This document ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and provides a clear framework for executing a consistent, thorough testing process.
Data quality in a data warehouse is ensured through various techniques, including data validation, profiling, data governance, and continuous monitoring and improvement.